Orchestrating Application and Database Changes
Modern applications are tightly coupled with the databases they rely on. Deploying a new version of an application often requires a corresponding schema update in the database. If these two changes are not coordinated properly, it can lead to application downtime, data inconsistencies, or failed deployments.
By combining Harness CD for application delivery and Harness Database DevOps for schema management, you can orchestrate database and application changes in a single pipeline in a single pipeline. In this guide, we'll walk through the process of creating a pipeline that coordinates both application and database changes.
Why Coordinate App and DB Deployments?
- Eliminate drift: Prevent mismatches between application code and database schema.
- Zero downtime: Support phased rollouts with pre-validated schema updates.
- Rollback safety: Roll back both schema and app changes if deployment fails.
- Single source of truth: Manage all change logic in one pipeline.
Pipeline Design Principles
When creating a pipeline that coordinates both application and database changes, consider the following steps:
- Clone Application and Schema Repositories – Fetch the application code and database migration scripts.
- Apply Database Schema Changes – Execute schema migrations aligned with the application version.
- Deploy the Application – Roll out changes to Kubernetes or another runtime environment.
- Rollback Strategy – Define how to roll back schema or application if issues occur.
Example Workflow
- Visual
- Yaml
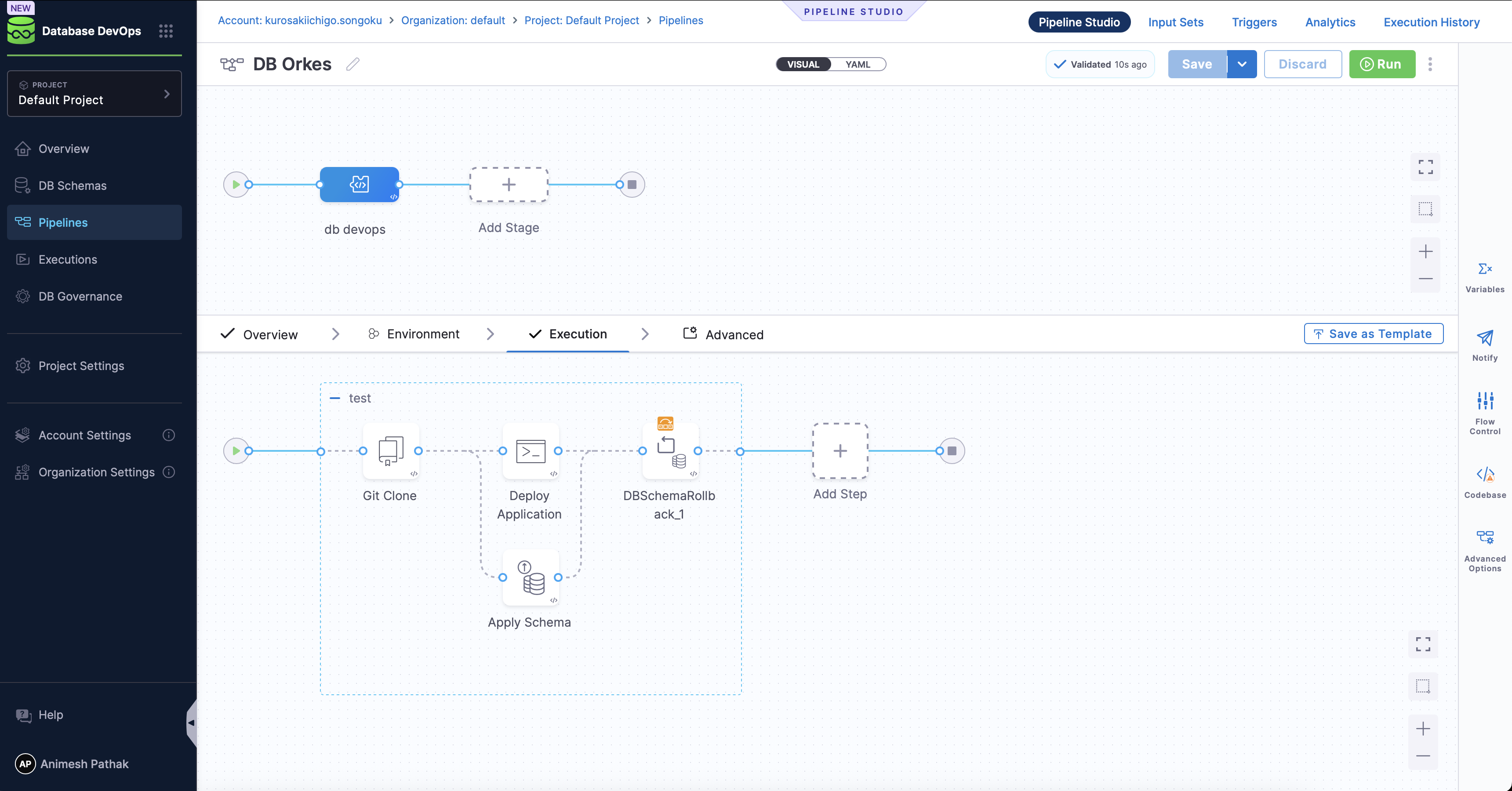
Harness Database DevOps introduces native steps like DBSchemaApply and DBSchemaRollback for executing and reversing schema migrations safely within a pipeline.
pipeline:
name: DB Orkes
identifier: DB_Orkes
projectIdentifier: default_project
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
stages:
- stage:
name: db devops
identifier: db_devops
description: ""
type: Custom
spec:
execution:
steps:
- stepGroup:
name: test
identifier: test
steps:
- step:
type: GitClone
name: Git Clone
identifier: Git_Clone
spec:
connectorRef: demodb
repoName: orkes
build:
type: branch
spec:
branch: main
- parallel:
- step:
type: Run
name: Deploy Application
identifier: Deploy_Application
spec:
connectorRef: dockerHarness
image: bitnami/kubectl:latest
shell: Bash
command: |-
cd orkes
echo "Deploying app from GitLab Container Registry..."
kubectl apply -f deployment.yml
kubectl rollout status deployment/go-mongodb-app
failureStrategies:
- onFailure:
errors:
- Timeout
action:
type: Ignore
- step:
type: DBSchemaApply
name: Apply Schema
identifier: Apply_Schema
spec:
connectorRef: account.harnessImage
dbSchema: DB_Orkes
dbInstance: mongorelease
tag: v1.0.0
changeSetFailureStrategy: MARK_NEXT_RUN
timeout: 10m
- step:
type: DBSchemaRollback
name: DBSchemaRollback_1
identifier: DBSchemaRollback_1
spec:
connectorRef: account.harnessImage
dbSchema: DB_Orkes
dbInstance: mongorelease
changeSetCount: 1
timeout: 10m
when:
stageStatus: Failure
stepGroupInfra:
type: KubernetesDirect
spec:
connectorRef: db
rollbackSteps: []
serviceDependencies: []
tags: {}
While some teams run schema and application deployments in parallel to save time, we recommend applying schema changes first to ensure backward compatibility and reduce deployment risks
Key Highlights
- Parallel Execution: Application deployment and schema migrations can run in parallel to reduce deployment time.
- Schema Failure Strategy: Use failure strategies such as marking failed changesets for rollback continuity.
- Rollback Support: Schema rollback ensures recovery when deployments fail or validation errors are detected.
- Kubernetes Native: Direct cluster access simplifies application rollouts and coordination.
Best Practices
- Backward-Compatible Schema Changes - Always design schema updates that can work with older application versions.
- Feature Flags - Gate new features until the schema change is fully deployed and validated.
- Version Alignment - Tag schema migrations (e.g.,
v1.0.0,v1.0.1) to match application releases. - Progressive Rollouts - Combine with deployment strategies like blue/green or canary rollouts.
- Automated Rollbacks - Test rollback flows regularly to ensure recovery is reliable.
Conclusion
By orchestrating application and database changes together in Harness pipelines, you can deliver faster, safer, and more resilient deployments. This approach removes the risks of mismatched deployments and provides a single automated flow for managing complex, interdependent changes.