(STO license) Create a build-scan-push pipeline
This topic describes how to create an end-to-end pipeline that builds an image and pushes it to Docker Hub only if the codebase and image contain no critical vulnerabilties. This pipeline uses two free tools:
-
Semgrep, a popular SAST tool for detecting vulnerabilities in application code. Semgrep can scan a wide variety of languages and includes a free version for individuals who want to scan files locally.
-
Aqua Trivy, a popular open-source tool for scanning container images.
Once you complete this workflow, you'll have a complete end-to-end pipeline that you can easily adapt to a wide variety of use cases. You can also copy/paste the YAML pipeline example below into Harness and update it with your own infrastructure, connectors, and access tokens.
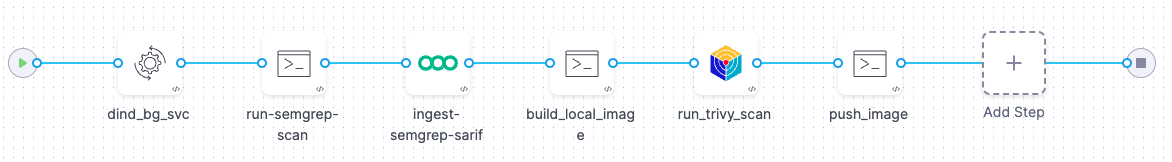
The following steps describe the workflow:
-
A Run step scans the codebase using Semgrep and saves the results to a SARIF file.
-
A Semgrep step ingests the scan results (ingestion-only workflow).
-
If the code has no critical vulnerabilities, another Run steps builds the image.
-
An Aqua Trivy step scans the image and ingests the results (orchestration workflow).
-
If the image has no critical vulnerabilities, another Run step pushes the image to Docker Hub.
-
This workflow has the following prerequisites:
-
A Harness account and STO module license.
-
You must have a Security Testing Developer or AppSec role assigned.
-
A basic understanding of key STO concepts and good practices is recommended. This workflow builds on the SAST code scans using Semgrep and Container image scans with Aqua Trivy workflows.
-
A Semgrep account login and access token. For specific instructions, go to Getting started from the CLI in the README on GitHub.
-
GitHub requirements — This workflow assumes you have the following:
-
A GitHub account and access token.
-
A GitHub connector that specifies your account (
http://github.com/my-account) but not a specific repository (http://github.com/my-account/my-repository). -
Your GitHub account should include a repository with code in a language supported by Semgrep such as Python or NodeJS. The repo should also include a Dockerfile for creating an image.
This workflow uses the dvpwa repository as an example. The simplest setup is to fork this repository into your GitHub account.
-
-
Docker requirements — The last step in this pipeline pushes the built image to your image registry. To do this step, you must have the following:
- A Docker Hub account and access token.
- A Docker connector is required to push the image.
-
Your Semgrep, GitHub, and Docker Hub access tokens must be stored as Harness secrets.
-
Set up your pipeline
Do the following:
-
Select Security Testing Orchestration (left menu, top) > Pipelines > Create a Pipeline. Enter a name and click Start.
-
In the new pipeline, select Add stage > Security.
-
Set up your stage as follows:
-
Enter a Stage Name.
-
Disable Clone Codebase. You will add a Run step to clone the codebase later.
-
-
In the Pipeline Editor, go to Overview and add the following shared path:
/shared/customer-artifactsYou'll use this shared folder to store the code repo so that all steps can access it.
-
Go to Overview and add the following Shared Path:
/shared/scan_results -
Expand Overview > Advanced and add the following stage variables.
You'll be specifying runtime inputs for some of these variables. This enables you to specify the code repo, branch, image label, and image tag, and other variables at runtime.
-
GITHUB_USERNAME— Select Secret as the type and enter your GitHub login name. -
GITHUB_PAT— Select Secret as the type and then select the Harness secret for your GitHub access token. -
GITHUB_REPO— Select String for the type and Runtime Input for the value (click the "tack button" to the right of the value field). -
GITHUB_BRANCH— Select String and Runtime Input. -
DOCKERHUB_USERNAME— Select String as the type and enter your DockerHub login name. -
DOCKERHUB_PAT— Select Secret as the type and then select the Harness secret for your Docker Hub access token. -
DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL— Select String and Runtime Input. -
DOCKER_IMAGE_TAG— Select String and Runtime Input.
-
-
In the Pipeline Editor, go to Infrastructure and select Cloud, Linux, and AMD64 for the infrastructure, OS, and architecture.
You can also use a Kubernetes or Docker build infrastructure, but these require additional work to set up. For more information, go to Set up a build infrastructure for STO.
The following step is required for Kubernetes or Docker infrastructures only. If you're using Harness Cloud, go to Add the codebase scan step.
Add a Docker-in-Docker background step
The following use cases require a Docker-in-Docker background step in your pipeline:
- Container image scans on Kubernetes and Docker build infrastructures
- Required for Orchestration and Dataload scan modes
- Custom Scan steps on Kubernetes and Docker build infrastructures
- Required for all target types and Orchestration/DataLoad modes
The following use cases do not require a Docker-in-Docker background step:
- Harness Cloud AMD64 build infrastructures
- SAST/DAST/configuration scans that use a scanner-specific step and not a Custom Scan step.
- Ingestion scans where the data file has already been generated
Set up a Docker-in-Docker background step
-
Go to the stage where you want to run the scan.
-
In Overview, add the shared path
/var/run. -
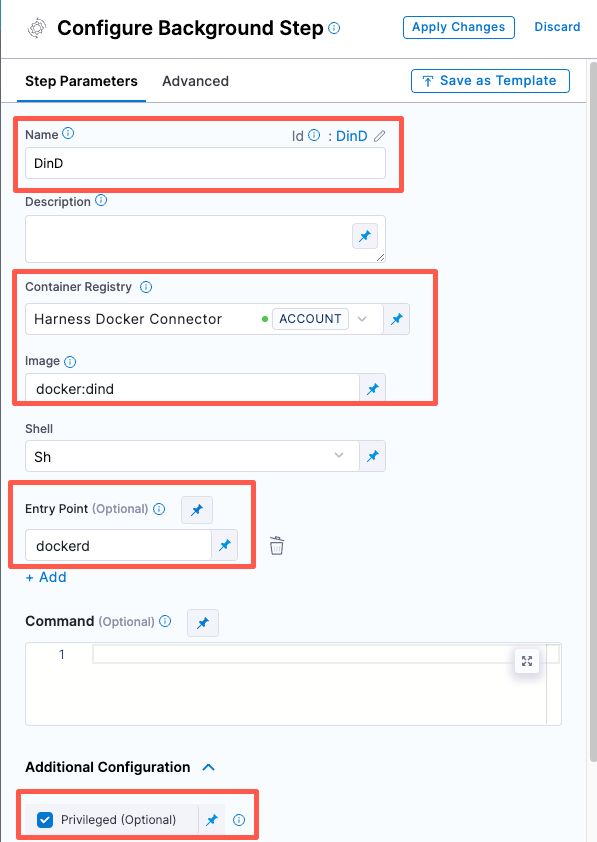
In Execution, do the following:
- Click Add Step and then choose Background.
- Configure the Background step as follows:
-
Dependency Name =
dind -
Container Registry = The Docker connector to download the DinD image. If you don't have one defined, go to Docker connector settings reference.
-
Image =
docker:dind -
Under Entry Point, add the following:
dockerdIn most cases, using
dockerdis a faster and more secure way to set up the background step. For more information, go to the TLS section in the Docker quick reference.If the DinD service doesn't start with
dockerd, clear the Entry Point field and then run the pipeline again. This starts the service with the default entry point. -
Under Additional Configuration, select the Privileged checkbox.
-
- Visual setup
- YAML setup
Add a Background step to your pipeline and set it up as follows:
- step:
type: Background
name: background-dind-service
identifier: Background_1
spec:
connectorRef: CONTAINER_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: docker:dind
shell: Sh
entrypoint:
- dockerd
privileged: true
Add the codebase scan step
Now you will add a step that runs a scan using the local Semgrep container image maintained by Harness.
- Visual
- YAML
-
Go to Execution and add a Run step.
-
Configure the step as follows:
-
Name = run_semgrep_scan
-
Command =
# install git
apk add git
git --version
# clone repo, cd to local clone, check out branch
cd /shared/scan_results
git clone https://github.com/<+stage.variables.GITHUB_USERNAME>/<+stage.variables.GITHUB_REPO>
cd /shared/scan_results/<+stage.variables.GITHUB_REPO>
git checkout <+stage.variables.GITHUB_BRANCH>
# run semgrep scan, save results to SARIF file
semgrep --sarif --config auto -o /shared/scan_results/semgrep.sarif -
Open Optional Configuration and set the following options:
-
Container Registry — When prompted, select Account and then
Harness Docker Connector. The step uses this connector to download the scanner image. -
Image = returntocorp/semgrep
-
Add the following environment variable:
-
Key :
SEMGREP_APP_TOKEN -
Value : Click the type selector (right), set the value type to Expression, and enter the value
<+secrets.getValue("YOUR_SEMGREP_TOKEN_SECRET")>.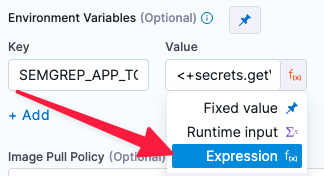
-
-
-
Add a Run step to your SecurityTests stage and configure it as follows:
-
type:Run -
name:A name for the step. -
identifier:A unique step ID. -
spec :-
connectorRef : account.HarnessImageThis is a connector to the Harness image registry. The step uses this connector to download the scanner image.
-
image : returntocorp/semgrep -
shell : Sh -
command : |-
# install git
apk add git
git --version
# clone repo, cd to local clone, check out branch
cd /shared/scan_results
git clone https://github.com/<+stage.variables.GITHUB_USERNAME>/<+stage.variables.GITHUB_REPO>
cd /shared/scan_results/<+stage.variables.GITHUB_REPO>
git checkout <+stage.variables.GITHUB_BRANCH>
# run semgrep scan, save results to SARIF file
semgrep --sarif --config auto -o /shared/scan_results/semgrep.sarif -
envVariables:SEMGREP_APP_TOKEN: <+secrets.getValue("YOUR_SEMGREP_TOKEN_SECRET")>
-
Here's an example:
- step:
type: Run
name: run-semgrep-scan
identifier: Run_1
spec:
connectorRef: account.harnessImage
image: returntocorp/semgrep
shell: Sh
command: |-
# install git
apk add git
git --version
# clone repo into shared folder, cd to local clone, check out branch
cd /shared/scan_results
git clone https://github.com/<+stage.variables.GITHUB_USERNAME>/<+stage.variables.GITHUB_REPO>
cd /shared/scan_results/<+stage.variables.GITHUB_REPO>
git checkout <+stage.variables.GITHUB_BRANCH>
# run semgrep scan, save results to SARIF file
semgrep --sarif --config auto -o /shared/scan_results/semgrep.sarif
# cat /shared/scan_results/semgrep.sarif
envVariables:
SEMGREP_APP_TOKEN: <+secrets.getValue("semgrepkey")>
Add the Semgrep ingest step
Now that you've added a step to run the scan, it's a simple matter to ingest it into your pipeline. Harness provides a set of customized steps for popular scanners such as Semgrep.
It's generally good practice to set the fail_on_severity for every scan step. Leave this setting at None for now so you can run and test the entire-end-to-end workflow.
- Visual
- YAML
-
In Execution, add a Semgrep step after your Run step.
-
Configure the step as follows:
-
Name =
ingest_semgrep_data -
Type = Repository
-
Under Target:
-
Name = Select Runtime Input as the value type.
-
Variant = Select Runtime Input as the value type.
-
-
Ingestion File =
/shared/scan_results/semgrep.sarif
-
Add a step after the Run step and configure it as follows:
type:Semgrepname:A name for the step.identifier:A unique step ID.spec :mode :ingestionconfig: defaulttarget :name : <+stage.variables.GITHUB_REPO>type : repositoryvariant : <+stage.variables.GITHUB_BRANCH>When scanning a repository, you will generally use the repository name and branch for the target name and variant.
advanced :log :level : infofail_on_severity: none
ingestion :file : /shared/scan_results/semgrep.sarif
Here's a YAML example:
- step:
type: Semgrep
name: ingest_semgrep_data
identifier: ingest_semgrep_data
spec:
mode: ingestion
config: default
target:
name: <+stage.variables.GITHUB_REPO>
type: repository
variant: <+stage.variables.GITHUB_BRANCH>
advanced:
log:
level: debug
fail_on_severity: critical
ingestion:
file: /shared/scan_results/semgrep.sarif
Run the pipeline and verify your results
This is a good time to run your pipeline and verify that it can scan the repo and ingest the results correctly.
-
Click Run and set the
GITHUB_REPOandGITHUB_BRANCHvariables. (You don't need to set the image variables.)If you forked the dvpwa repository repo into your GitHub account and want to use that, set the fields like this:
GITHUB_REPO= dvpwaGITHUB_BRANCH= master
-
Click Run Pipeline and wait for the execution to finish. You can then view your scan results in Vulnerabilities tab.
Add the image build step
Assuming that the Semgrep scanner detected no critical vulnerabilities, the next step is to build a local image using the Dockerfile in your codebase.
- Visual
- YAML
-
Add a Run step after the Semgrep ingest step.
-
Configure the step as follows:
-
Name = build_local_image
-
Command =
# wait until the dind service is available
while ! docker ps ;do
echo "Docker not available yet"
done
echo "Docker service is ready"
docker ps
# cd to the repo and build/tag the local image
cd /shared/scan_results/<+stage.variables.GITHUB_REPO>
docker login \
--username="<+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>" \
--password="<+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_PAT>" \
docker build -t <+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL> . \
docker tag \
<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL> \
<+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL>:<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_TAG> -
Open Optional Configuration and set the following options:
-
Container Registry — When prompted, select Account and then your Docker Hub connector.
-
Image = docker
-
-
Add a Run step and configure it as follows:
-
type:Run -
name:A name for the step. -
identifier:A unique step ID. -
spec :-
connectorRef : YOUR_DOCKERHUB_CONNECTOR -
image : returntocorp/semgrep -
shell : Sh -
command : |-
# install git
apk add git
git --version
# clone repo, cd to local clone, check out branch
cd /shared/scan_results
git clone https://github.com/<+stage.variables.GITHUB_USERNAME>/<+stage.variables.GITHUB_REPO>
cd /shared/scan_results/<+stage.variables.GITHUB_REPO>
git checkout <+stage.variables.GITHUB_BRANCH>
# run semgrep scan, save results to SARIF file
semgrep --sarif --config auto -o /shared/scan_results/semgrep.sarif -
envVariables:SEMGREP_APP_TOKEN: <+secrets.getValue("YOUR_SEMGREP_TOKEN_SECRET")>
-
Here's an example:
- step:
type: Run
name: build_local_image
identifier: build_local_image
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: docker
shell: Sh
command: |-
# wait until the docker service is available
while ! docker ps ;do
echo "Docker not available yet"
done
echo "Docker service is ready"
# build and tag the local image
cd /shared/scan_results/<+stage.variables.GITHUB_REPO>
docker login --username="<+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>" --password="<+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_PAT>"
docker build -t <+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL> .
docker tag <+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL> <+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL>:<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_TAG>
docker image ls
privileged: true
Add the Aqua-Trivy scan/ingest step
- Visual
- YAML
Add an Aqua Trivy step to your pipeline after the build step and configure it as follows:
-
Scan Mode = Orchestration In orchestrated mode, the step runs the scan and ingests the results in one step.
-
Target name — Click the "tack" button on the right side of the input field and select Expression. Then enter the following expression:
<+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL> -
Target variant — Select Expression for the value type, then enter the following expression:
<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_TAG> -
Container image Type = Local Image
-
Container image name — Select Expression for the value type, then enter the following expression:
<+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL> -
Container image tag — Select Expression for the value type, then enter the following expression:
<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_TAG> -
Fail on Severity = None
Add an Aqua Trivy step to your pipeline after the build step and configure it as follows:
type:AquaTrivyname:A name for the step.identifier:A unique step ID.spec :mode :orchestrationIn orchestrated mode, the step runs the scan and ingests the results in one step.config: defaulttarget :name : <+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL>type : containervariant : <+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_TAG>When scanning an image, you generally use the image label and tag for the target name and variant .advanced :log :level : infofail_on_severity: critical
privileged: trueimage:type: local_imagename: <+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL>tag: <+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_TAG>
Here's an example:
- step:
type: AquaTrivy
name: run_trivy_scan
identifier: AquaTrivy_1
spec:
mode: orchestration
config: default
target:
name: <+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL>
type: container
variant: <+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_TAG>
advanced:
log:
level: info
fail_on_severity: critical
privileged: true
image:
type: local_image
name: <+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL>
tag: <+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_TAG>
Run the pipeline and verify your results
This is a good time to run your pipeline and verify that it can scan the repo and ingest the results correctly.
-
Click Run and set the GitHub and Docker variables. (You don't need to set the image variables.)
If you forked the dvpwa repository repo into your GitHub account and want to use that, set the fields like this:
GITHUB_REPO= dvpwaGITHUB_BRANCH= masterDOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL= dvpwaDOCKER_IMAGE_TAG= master-scantest-DONOTUSE
tipInput sets enable you to reuse a single pipeline for multiple scenarios. You can define each scenario in an input set and then select the relevant input setat runtime. To save these inputs, click Save as New Input Set.
-
Click Run Pipeline and wait for the execution to finish. You can then view your scan results, for both the repo and the image, in Vulnerabilities tab.
Add the image push step
Assuming that the Aqua Trivy scanner detected no critical vulnerabilities, you can now push your new image to Docker Hub.
- Visual
- YAML
-
Add a Run step after the Aqua Trivy scan/ingest step.
-
Configure the step as follows:
-
Name = push_image
-
Command =
# if the image passed the scan,
# push it to the image registry
docker login --username="<+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>" --password="<+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_PAT>"
docker push <+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL>:<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_TAG> -
Open Optional Configuration and set the following options:
-
Container Registry — Select your Docker Hub connector.
-
Image = docker
-
-
Add a Run step after the Bandit scan step and configure it as follows:
-
type:Run -
name:A name for the step. -
identifier:A unique step ID. -
spec :-
connectorRef : MY_DOCKERHUB_CONNECTOR -
image : docker -
shell : Sh -
command : |-
# if the image passed the scan,
# push it to the image registry
docker login --username="<+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>" --password="<+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_PAT>"
docker push <+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL>:<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_TAG>
-
Here's an example:
- step:
type: Run
name: push_image
identifier: push_image
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: docker
shell: Sh
command: |-
# if the image passed the scan,
# push it to the image registry
docker login --username="<+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>" --password="<+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_PAT>"
docker push <+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL>:<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_TAG>
YAML pipeline example
Here's an example of the pipeline you created in this workflow. If you copy this example, replace the placeholder values with appropriate values for your project, organization, and connectors.
pipeline:
projectIdentifier: YOUR_HARNESS_PROJECT_ID
orgIdentifier: YOUR_HARNESS_ORGANIZATION_ID
tags: {}
stages:
- stage:
name: scan_codebase
identifier: scan_codebase
type: SecurityTests
spec:
cloneCodebase: false
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: Run
name: run-semgrep-scan
identifier: Run_1
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: returntocorp/semgrep
shell: Sh
command: |-
# install git, clone the code repo, and cd to the local clone
apk add git
git --version
cd /shared/scan_results
git clone https://github.com/<+stage.variables.GITHUB_USERNAME>/<+stage.variables.GITHUB_REPO>
cd /shared/scan_results/<+stage.variables.GITHUB_REPO>
git checkout <+stage.variables.GITHUB_BRANCH>
semgrep --sarif --config auto -o /shared/scan_results/semgrep.sarif
# cat /shared/scan_results/semgrep.sarif
envVariables:
SEMGREP_APP_TOKEN: <+secrets.getValue("semgrepkey")>
resources:
limits:
memory: 4096M
- step:
type: Semgrep
name: ingest-semgrep-sarif
identifier: Semgrep_1
spec:
mode: ingestion
config: default
target:
name: <+stage.variables.GITHUB_REPO>
type: repository
variant: <+stage.variables.GITHUB_BRANCH>
advanced:
log:
level: info
fail_on_severity: critical
ingestion:
file: /shared/scan_results/semgrep.sarif
- step:
type: Run
name: build_local_image
identifier: build_local_image
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: docker
shell: Sh
command: |-
# wait until the dind service is available
while ! docker ps ;do
echo "Docker not available yet"
done
echo "Docker service is ready"
docker ps
# build and tag the local image
cd /shared/scan_results/<+stage.variables.GITHUB_REPO>
docker login --username="<+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>" --password="<+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_PAT>"
docker build -t <+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL> .
docker tag <+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL> <+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL>:<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_TAG>
docker image ls
privileged: false
- step:
type: AquaTrivy
name: run_trivy_scan
identifier: AquaTrivy_1
spec:
mode: orchestration
config: default
target:
name: <+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL>
type: container
variant: <+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_TAG>
advanced:
log:
level: info
fail_on_severity: critical
privileged: true
image:
type: local_image
name: <+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL>
tag: <+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_TAG>
sbom:
format: spdx-json
- step:
type: Run
name: push_image
identifier: push_image
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: docker
shell: Sh
command: |-
# if the image passed the scan,
# push it to the image registry
docker login --username="<+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>" --password="<+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_PAT>"
docker push <+stage.variables.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL>:<+stage.variables.DOCKER_IMAGE_TAG>
privileged: true
sharedPaths:
- /var/run
- /shared/scan_results
caching:
enabled: false
paths: []
slsa_provenance:
enabled: false
platform:
os: Linux
arch: Amd64
runtime:
type: Cloud
spec: {}
variables:
- name: GITHUB_USERNAME
type: String
description: ""
value: mygithubusername
- name: GITHUB_PAT
type: Secret
description: ""
value: mygithubpatstosecret
- name: GITHUB_REPO
type: String
description: ""
value: <+input>
- name: GITHUB_BRANCH
type: String
description: ""
required: false
value: <+input>
- name: DOCKERHUB_USERNAME
type: String
description: ""
value: mydockerhubusername
- name: DOCKERHUB_PAT
type: Secret
description: ""
value: mydockerhubpat
- name: DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL
type: String
description: ""
value: <+input>
- name: DOCKER_IMAGE_TAG
type: String
description: ""
required: false
value: <+input>
description: ""
timeout: 10m
notificationRules: []
identifier: v5_sbsp_workflow
name: v5_sbsp_workflow